Troubleshooting
Wake-on-LAN can be a frustrating technology to implement. This is because it requires appropriate BIOS, network card and, sometimes, operating system and router support to function reliably. In some cases, hardware may wake from one low power state but not from others. This means that due to hardware issues the computer may be waking up from the “fully off state” (S5) but doesn’t wake from sleep or hibernation or vice-versa. Also, it is not always clear what kind of magic packet a NIC expects to see.
WOL includes features to make it easier to configure and troubleshoot.
Aquila WOL includes a built-in packet analyzer to help you determine if your packets are being received correctly. You may install the WOL application on the host you are trying to wake up, and run Tools -> Listen. The Listener window will display all WOL packets heard on this machine. It will show packets from any WOL software, not only Aquila WOL.
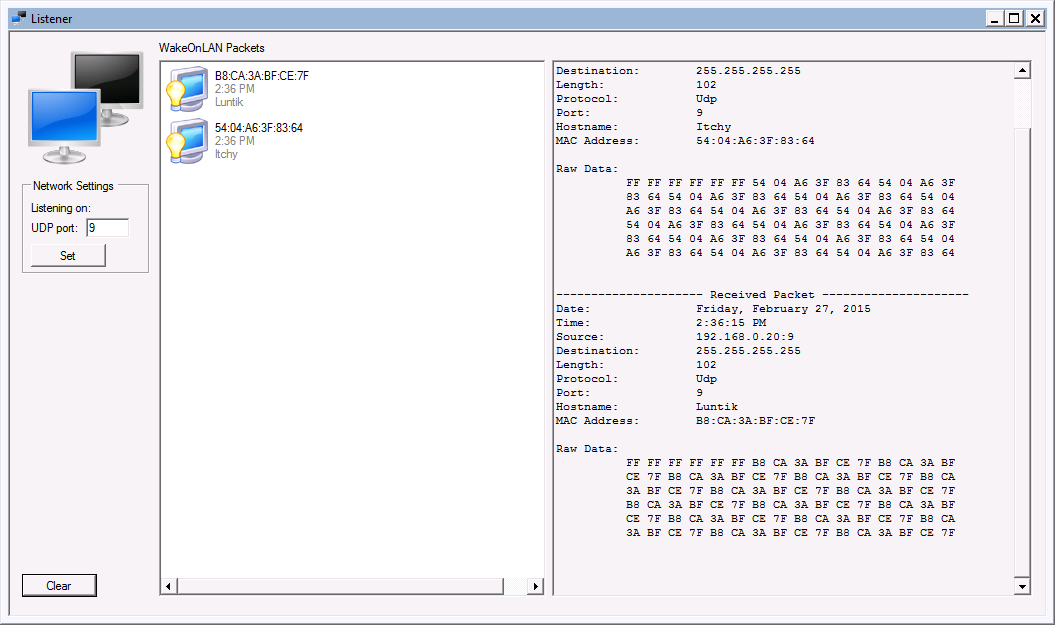
Some computers may have port 9 locked which will result in an error message when trying to run the Listener. See here for additional information. Configuring WOL correctly means finding IP addresses and MAC addresses for the hosts you are trying to control. Aquila WOL includes tools to make this easy and avoid mistakes. Access the search tool from the main window by clicking Tools -> Search for machines. Detailed help on the search tool is available here.
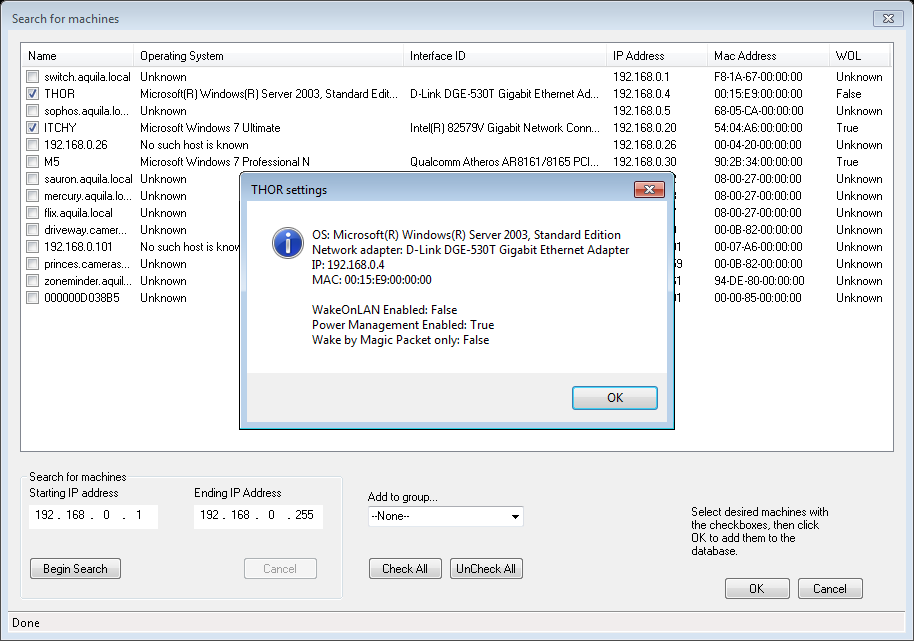
Aquila WOL consists of several different parts
- Wake up. Waking up a host requires the correct MAC address and broadcast subnet be configured.
- Shutdown. Shutdown requires the netbios name or IP address for WOL to contact the host to shut it down. It requires that you have rights to shutdown the host, Administrator or Power-User rights, for example. Shutdown does not use the MAC address. Shutdown for non-windows hosts requires that you use the shutdown command line field. Sleep and Hibernate are Windows-only functions. Please note that depending on the power scheme on your host computer, a hibernate command may invoke sleep instead, or a sleep command may invoke hibernate.
- Host status in the main window. The main window displays the host status using either the IP address or netbios name. It uses ICMP to determine if the host is online. It does not use the MAC nor does it require admin rights.
Firewall considerations
If there is a firewall between the WOL computer and the target host, you must configure it allow the necessary traffic through.
For Windows firewall on the target host, you would enable the following inbound rules:
For ping and status:
- File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request – ICMPv4-In)
For shutdown:
- Windows Firewall Remote Management (RPC)
- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI-In)
For popup messages:
- Distributed Transaction Coordinator (RPC)
The RPC server is unavailable (Exception from HRESULT: 0x800706BA)
If you get this error while trying to shutdown a Windows host, it means that WOL was not able to send the shutdown command to the host. The problem is one of these things.
- There is a local firewall running on the host that is blocking the RPC traffic. (See “Firewall Configuration”)
- There is a firewall or network issue on your network that is preventing the RPC traffic from reaching the remote host.
- You have the wrong host name or ip address specified in the host properties, so WOL is not sending the commands to the correct destination.
- The RPC services are not running on the host you are trying to shutdown.
- Your user account, or the userid and password you specified in the host properties does not have the proper credentials to shutdown the remote host.
Machine won’t wake up, NIC is not armed for WOL
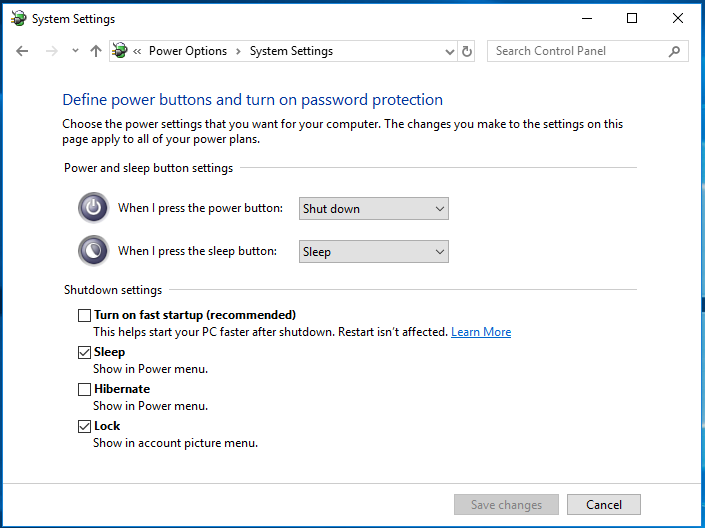
Try disabling Windows Fast Start
- Open Power Options
- Select “Choose what the power buttons do”
- Select “Change settings that are currently unavailable”
- Uncheck “Turn on fast startup”
Unable to open program?
In rare instances, your display configuration may have changed in such a way that the WOL program is trying to open “off screen”. This can be easily fixed by starting in Safe Mode. Another option would be to use “Reset Window Layout” which is available on the main menu, or the task tray menu. To access safe mode, hold down the Control key while starting WOL. Your display parameters will be reset to dafault. You will not lose any of your host-computer database.
Listener unable to access port
Wake-on-LAN uses UDP port 9 by default, to send WOL messages. This port is available for use on most Windows computers. However, if you have installed “Simple TCPIP services”, then Windows may be running the “discard” service. This service locks port 9 and will prevent the listener from connecting.
Go to Control Panel and disable the “Simple TCP/IP Services” service. You should now be able to run WOL without any conflict. If you suspect another program is using port 9, you can run netstat to find out which application has the port locked. The command “Netstat -ab” will list all of the ports that are in use. This must be run as Administrator. Look for the line following UDP 0.0.0.0:9. That will be the name of the application that is using port 9.
Program Crash
In the unlikely event that WOL crashes without displaying an error message, it will leave a crash log file on your computer.
The file can be found here: C:\Users\[YourUserName]\AppData\Roaming\Aquila Technology\WakeOnLan\[VersionNumber]\WakeOnLan.log
For example: C:\Users\phil\AppData\Roaming\Aquila Technology\WakeOnLan\2.7.5.1\WakeOnLan.log
Please send us that file! It will help us fix the error.
